 A specification was issued by the Technische Luftrüstung (Technical
Air Armaments Board) in late January 1944 for the definitive night fighter.
Preliminary requirements were to be a top speed of 900 km/h (559 mph),
an endurance of four hours, armament consisting of four cannon and internally
mounted radar (FuG 240 or 244).
A specification was issued by the Technische Luftrüstung (Technical
Air Armaments Board) in late January 1944 for the definitive night fighter.
Preliminary requirements were to be a top speed of 900 km/h (559 mph),
an endurance of four hours, armament consisting of four cannon and internally
mounted radar (FuG 240 or 244).
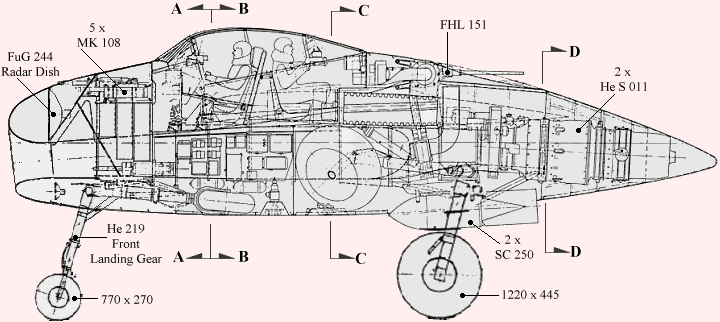
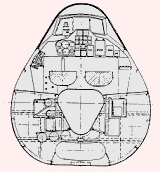
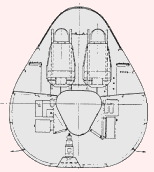
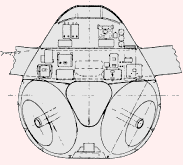
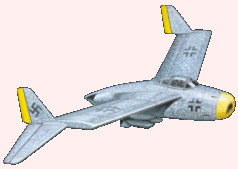
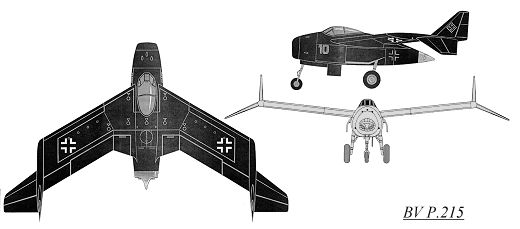
Dr. Richard Vogt, who designed the BV P.212, immediately began work on an aircraft to meet the specifications issued for the new night fighter. Vogt used the BV P.212 as the overall basis for the new BV P.215 night fighter. The fuselage was short, with an air intake in the nose leading directly to the two Heinkel He S 011 mounted in the rear fuselage. As with other Blohm & Voss Vogt designs, the fuselage structure was built up out of the intake tube, and all components attached to this structure (see the BV P.211.02). The wings featured a 30 degree sweepback and 6 degrees of dihedral; internally the support came from a wide wing box, constructed from welded steel. The outer wing tips angled down at 23 degrees, and assisted stability and control. Warm air diverted from the engine compartment was circulated through the wings for de-icing purposes. There were two small vertical fins and rudders located on the trailing edge of the wing, where the outer wing tips angled downwards. Total fuel capacity was 7800 liters (2061 gallons), stored mainly in wing tanks. An ingenious system to pre-heat the fuel was designed; a pump would circulate the fuel of the fuselage feeder tank through a spiral line around the engine compartment and into the wing tanks. The nose landing gear was taken from the Heinkel He 219 and retracted to the rear, and the two main wheels (angled forward by 16 degrees) also retracted forwards into the fuselage. The pressurized cockpit held a three man crew; a pilot, radar operator and navigator/radio man, and all three were provided with ejection seats. A wide variety of offensive armament could be carried in the aircraft's nose, and defensive armament consisted of a FHL 151 remote controlled, rear-facing turret armed with either one or two MG 151/20 20 mm cannon. A provision was made for possibly mounting two MK 108 30 mm cannon firing upwards, located behind the cockpit. Two SC 250 250 kg (551 lbs) or SC 500 (1102 lbs) could be carried in a belly recess. The BV P.215's constuction was mainly of metal througout, except for wooden control surfaces and the aircraft's nose. The nose was made of wood because of the installed electrical equipment. The installed electrical radio/radar equipment is listed below.
In the original Blohm & Voss proposal, it was pointed out that the P.215 was easily transportable. After removing the wings, the fuselage would be easily transportable with no need for specialized lifting equipment. On February 27, 1945, the specifications were upgraded for the future nightfighters, which none of the competitors' aircraft were able to achieve.Although the P.215 would have had good performance figures, it too did not reach the new specifications either. Nevertheless, it was chosen for further development on March 20, 1945. The end of the war ended any further development of this novel aircraft.