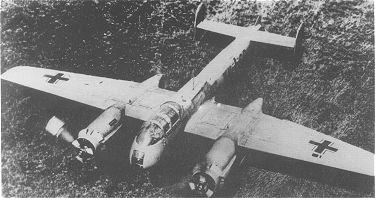

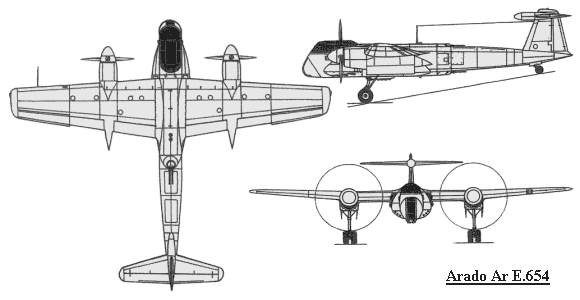
 The Arado Ar E.564 "Kampfzerstörer
" (destroyer, or heavy fighter) project was conceived by by Arado's Chief
Designer Dipl.-lng. Walter Blume. The fuselage was very similar to the
Ar 240
in appearance and construction, except it was widened to facilitate the
two Daimler Benz DB 614 or DB 627 engines which were mounted side-by-side
and inclined 15 degrees.. These engines drove the two propellers mounted
on the wing leading edges in small nacelles via a complicated and controversial
method. Basically, right angle gear boxes and long drive shafts connected
the propellers to the engines mounted in the fuselage. The advantages of
this system was to minimize drag caused by larger engine nacelles on the
wings and kept the engines in a more protected position within the fuselage.
The Arado Ar E.564 "Kampfzerstörer
" (destroyer, or heavy fighter) project was conceived by by Arado's Chief
Designer Dipl.-lng. Walter Blume. The fuselage was very similar to the
Ar 240
in appearance and construction, except it was widened to facilitate the
two Daimler Benz DB 614 or DB 627 engines which were mounted side-by-side
and inclined 15 degrees.. These engines drove the two propellers mounted
on the wing leading edges in small nacelles via a complicated and controversial
method. Basically, right angle gear boxes and long drive shafts connected
the propellers to the engines mounted in the fuselage. The advantages of
this system was to minimize drag caused by larger engine nacelles on the
wings and kept the engines in a more protected position within the fuselage.| Span | Length | Height |
Wing Area |
| 14.34 m 47' 1" |
12.81 m 42' 1" |
3.95 m 13' 0" |
31.3 m² 336.9 ft² |
| Arado Ar E.654 Models |
| There are no models of the Arado Ar E.654 available at the present time |

|

|
|
|

Above color illustration from Geheimprojekte der Luftwaffe Band III - Schlachtflugzeuge und Kampfzerstörer 1935-1945